Bot Rest API
Introduction
This article explains how to use the REST API response type in a bot. With this feature, you can integrate any third-party API without any coding.
In order to make it work, you need to set up two things:
- The REST API call itself
- A bot trigger that will use that call
- See an example of integration
- Also, your AI can return JSON directly for execution.
Rest API Call
The REST API call building window is built in such a way that you can execute almost any request you want.
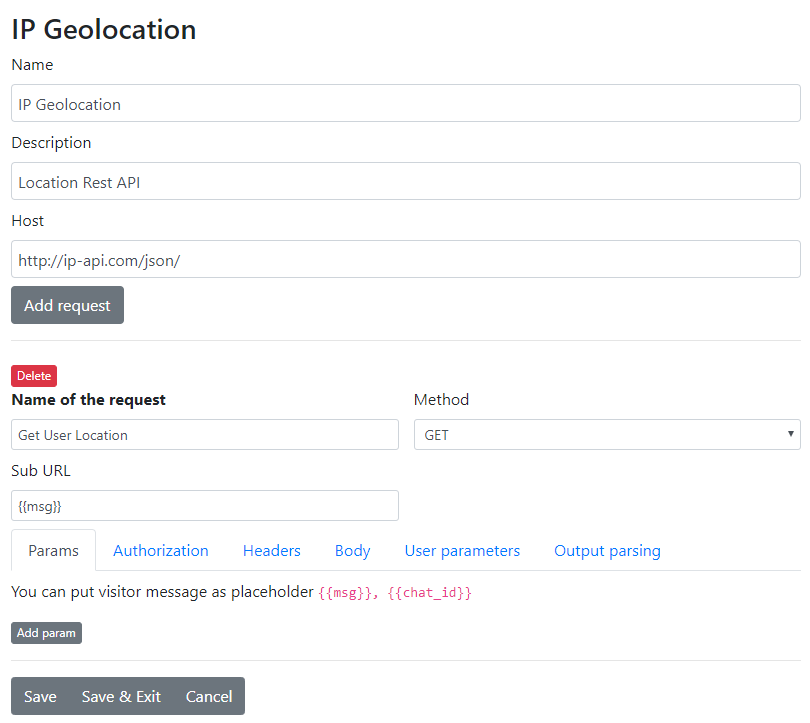
Fields Definition for REST API
Name
Name for your own purposes.
Description
Description for your own purposes.
Host
This should be a non-changing URL part. To this part, the Sub URL part is always appended.
Add request
This button adds new request options to this API. You can have as many requests as you want. The request name is visible in the trigger method choosing dropdown.
Request fields
Name of the request
Visible in the method choosing dropdown in the trigger.
Method
The appropriate method type for the request.
Sub URL
URL to append to the host. It can be one of the replaceable variables.
In this field URL can be urlencode_{{args.chat.nick}} or without escaped url {{args.chat.id}}. URL Encode should be used if URL contains spaces or in general, it's a query part of the URL.
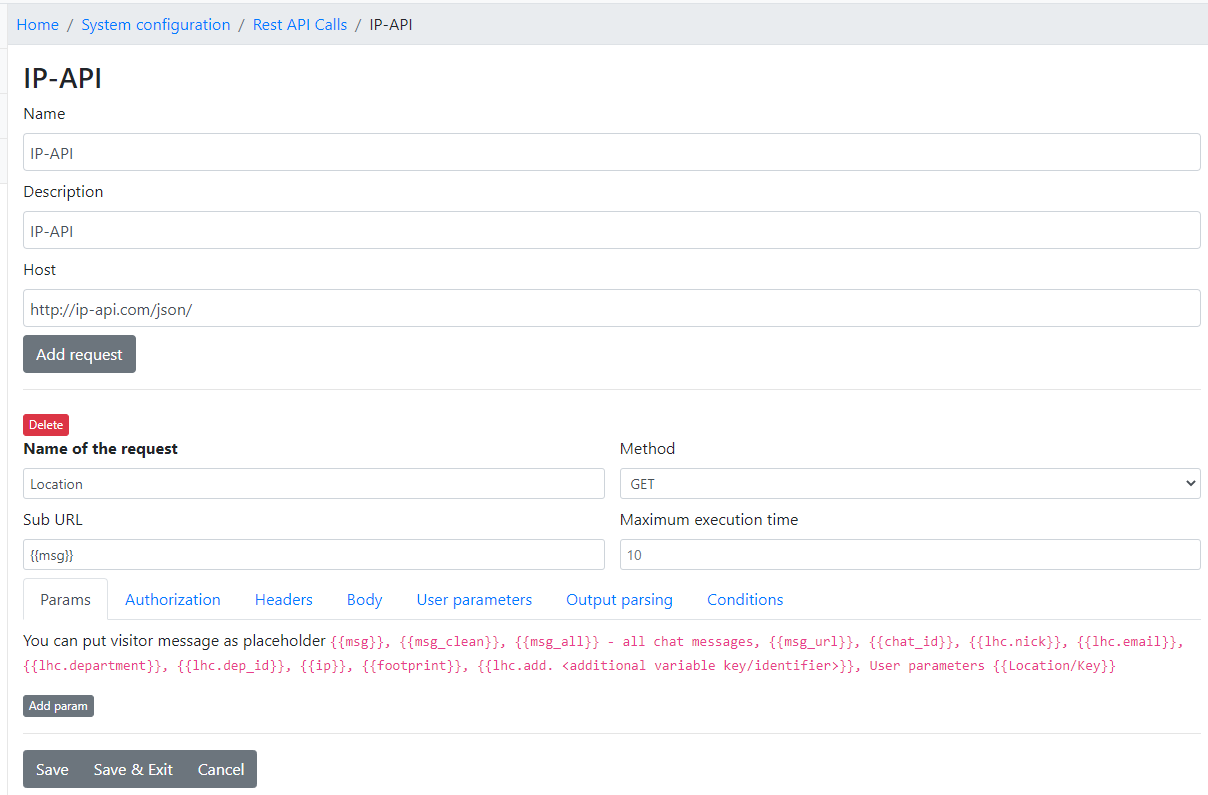
Split message into separate Rest API calls if message contains text and files at the same time.
It's an easy fix to send operator message containing files and text at the same time as a separate messages. It can be used for Telegram, WhatsApp, Messenger or any other Rest API where you think it would be usefull.
Params
In the Params section, you define arguments that should be accessible as GET parameters.
Authorization
If you are using an authorized API, you can set up basic authorization methods there.
Headers
These values will be added to the header. They are combined like this:
<Key>: <value>
Body
The body can be sent either as RAW, also known as JSON Body, or as regular POST parameters.
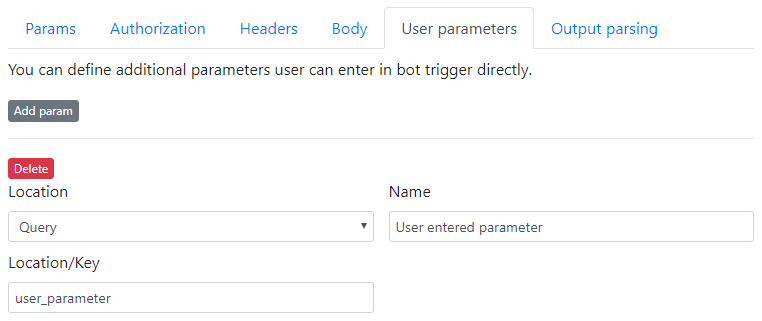
User parameters
These parameters can be entered directly in the bot trigger itself once the method is chosen.
If you choose Body Param, you can use this variable Location/Key as a replaceable variable in your body JSON content.
{{<Location/Key>}}
If you choose Query or Body Post Param, the key will be used as a post/get parameter directly.
In Rest API
In the trigger, it would look like
Output parsing
Output parsing is dedicated to extracting useful variables from the API response.
Name
The name will be visible within the option to execute a specific trigger based on the response.
In the trigger, it will be visible here
HTTP status code E.g 200,301,500
For this response to match, you can define the expected HTTP status code. It's optional. This way you can separate the success response from the failed one.
Response Location 1/2/3/4/5/6.
If you define a success location, it will parse the response as JSON and try to extract the specified attribute.
Examples of variable extraction:
status as location value would return success
{
"status": "success"
}
response:location as a location value would return Lithuania
{
"response": {
"location" : "Lithuania"
}
}
items:0:name as a location value would return Sub item name
{
"items": [
{
"name" : "Sub item name"
}
]
}
links:link:[type=forms]:url as a location value would return an element where the type is forms
{
"links": {
"link": [
{
"type": "prices",
"url": {},
"chat_message": "We do not have that information available online. We could follow up with you directly to discuss."
},
{
"type": "forms",
"url": "https://livehelperchat.com",
"chat_message": "You can view and download our forms on this page"
}
]
}
}
output:0:content:0:text___json_text:summary converts text attribute content to json array and returns summary attribute.
{"output": [
{
"type": "message",
"id": "msg_67e5506f329481928e778a945cbfd439010aa033a24ce511",
"status": "completed",
"role": "assistant",
"content": [
{
"type": "output_text",
"text": "{\"summary\":\"Chat summary.\",\"sentiment\":\"positive\"}",
"annotations": []
}
]
}
]
}
links:link___array_pop:type returns last element in link array and returns type of it.
{
"links": {
"link": [
{
"type": "prices",
"url": {},
"chat_message": "We do not have that information available online. We could follow up with you directly to discuss."
},
{
"type": "forms",
"url": "https://livehelperchat.com",
"chat_message": "You can view and download our forms on this page"
}
]
}
}
Parsing array for the output
user_info:phones^implode=={n}would output phones array combined with new line character.user_info:phones^implode==[b]{item}[/b]{n}would output phones array wrapper with bold and new line character
{
"user_info": {
"phones": [
"111111",
"222222"
]
}
}
Parsing XML for the output
when you parse xml you should omit first tag and start from the second tag:
- use
pin:value, NOTresponse:pin:value
<response>
<pin>
<value>2222</value>
</pin>
....
</response>
Conditions checking
Sometimes it makes sense to check was something found based on response attribute. So you can define condition to check.
Here we expect that status value would be success.
JSON should look like this
{
"status": "success"
}
Meta msg location.
Here we can extract meta_msg if you provide Live Helper Chat compatible JSON response. Meta message will be used in chosen response trigger [text message] if this trigger does not have any meta message information.
{
"msg": "Standard message text from REST API",
"meta_msg": {
"content": {
"quick_replies": [
{
"type": "button",
"content": {
"name": "Rest API Button",
"payload": "rest_api_button"
}
}
]
}
}
}
In order for rest API to receive these clicks you should also check in trigger Default for unknown button click
Each trigger at the bottom has Show code button. This code is supported only by Execute trigger body response type. If you just want to build trigger and get code for response and reuse it, it's the response type you should use instead.
Conditions
Only if these conditions are met we will send Rest API request. Usefull in webhook cases.
Let say you want to send request only if chat happened with a bot?
Condition for that chat could look like
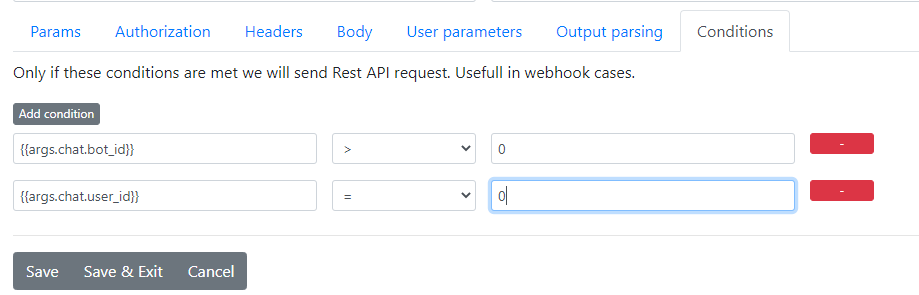
In case you want to send Rest API only if user message is not empty sample would look like
{{msg_clean_lowercase}} != // Do not enter anything
Polling
If you expect that the response will be delayed, you can set up polling. This way, the bot will keep checking the response until it matches one of the output combinations.
While doing, that web-server is keeping connection alive, which is not ideal for web application. It's better to use php-resque extension for that and have it happening in the background.
Sample bot and Rest-API https://github.com/LiveHelperChat/chatGPT/tree/main/doc/assistant for ChatGPT integration.
Streaming
Streaming allows to show visitor while tokens are generated on ChatGPT or any other platform which supports streaming.
Streaming event type field- In ChatGPT case it's returningevent: event.typetype response anddata:afterwards.
Requirements
- You have to have a background worker running. lhc-php-resque extension is optional but highly recommended. Otherwise you will be keeping connection to your web server.
- NodeJS-Helper server running. It is required.
- Before sending Rest API call in your bot make sure. Last message is a
Send typingmessage. We use typing message indicator and fill its content with streaming content.
Output parsing
Output is matched only if event is this type.If we want to match specific event for specificOutput combinationwe can set a filter for that.MessageReceivedevent as example is expectingthread.message.deltaas an example.- If this output combination result should be streamed you can check
Stream this outputcheckbox. This way it will be streamed to the visitor. Execute trigger on matched content. Stream will continue afterwards.- If you want just execute trigger and flow is expected to continue check this option.RunCreatedevent as example is expectingthread.run.createdas an example and expecting stream to continue. Messages will come afterward.If matched use response as final response.- If this output is matched it's response should be set as a final response. This happens inRequiresActionevent as an example. It's expectingthread.run.requires_actionas an example.Stream content as HTML.- If you want to stream content as HTML. We will render full HTML before feeding it to widget.- This should be checked for
ScheduleRun -> MessageReceived (output combination)andToolCallCompleted -> MessageReceived (output combination)events.
- This should be checked for
Sample bot and Rest-API https://github.com/LiveHelperChat/chatGPT/tree/main/doc/assistant_stream for ChatGPT integration.
Plain streaming
This is sample how to stream plain text to the visitor if API always is streaming data: content.
- Stream must follow
data: json_contentformat E.gdata: {"delta":"text chunk"} - Check
Streamingcheckbox in Rest API configuration Output parsingShould have at-least one combination defined.
Output parsing can look like this.
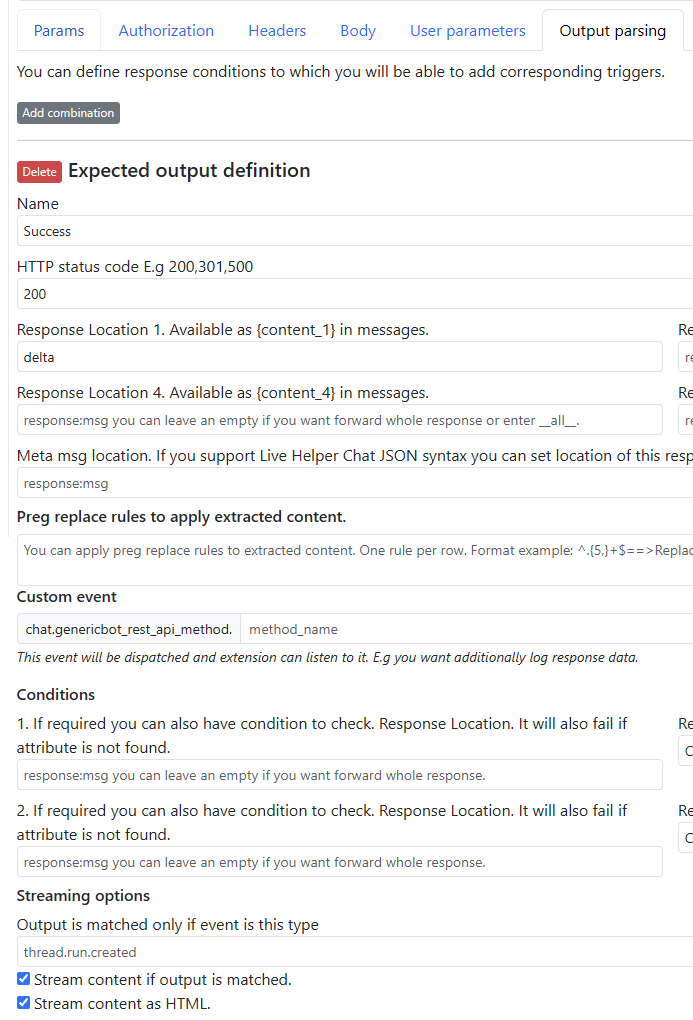
Body payload can look like this just
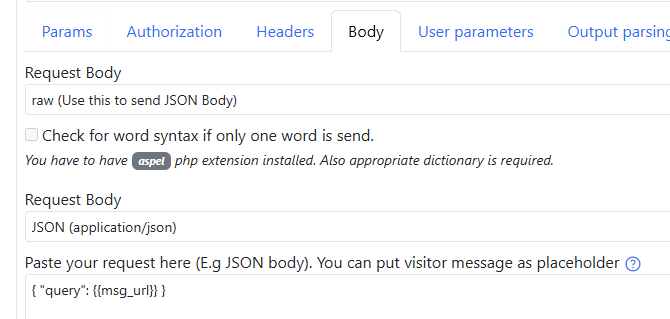
That's all your need to have in your Rest API configuration.
Trigger in bot can look like this.
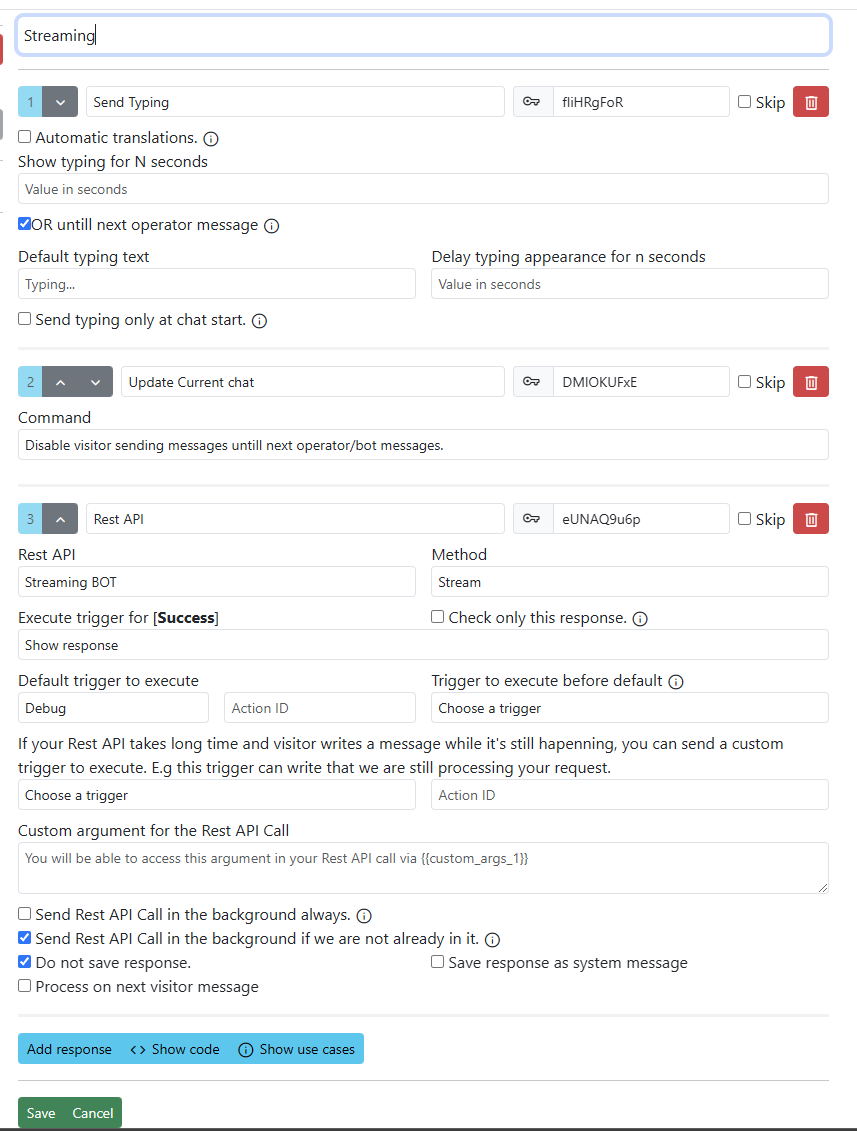
Show response trigger content
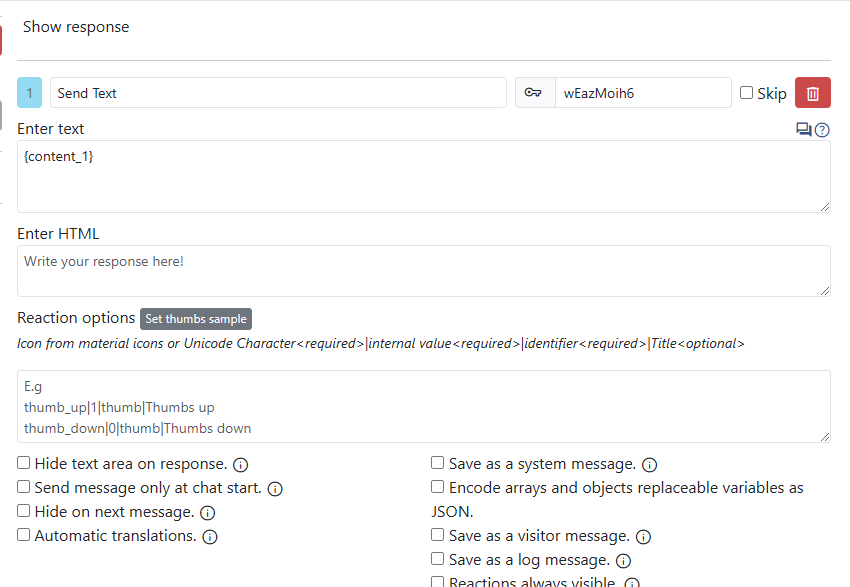
Replaceable variables
Rest API in value fields you can use these replaceable variables. These variables by default are already in json format with quotes.
All chat messages. These combinations are usefully in case you are implementing sentiment analysis and want for example determine the sentiment of operator/visitor or both messages:
You can quickly explore all possible chat attributes by clicking Explore possible chat attributes directly. link in Rest API builder interface next to Add request button. This option is also available in Audit Logs section.
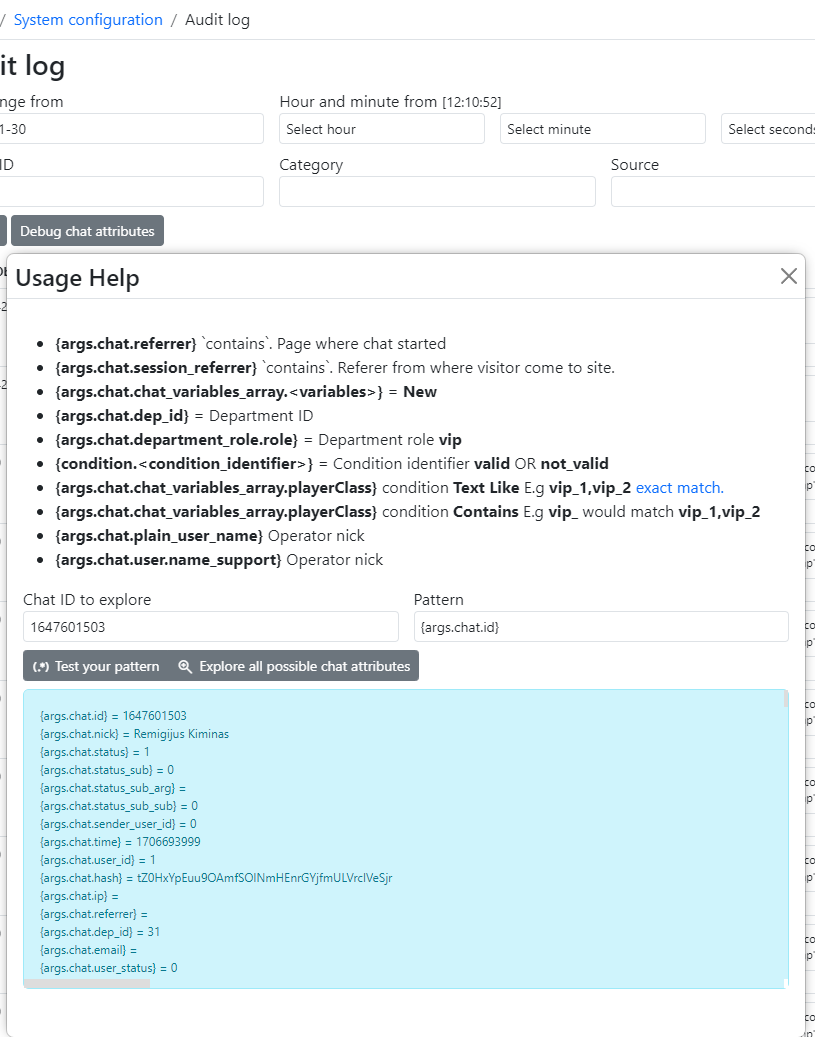
Single messages
{{msg}}- user/operator message.{{msg_lowercase}}- user/operator message. Lowercase version.{{msg_url}}- user/operator message will contain links instead of bbcode tags.{{msg_url_lowercase}}- user/operator message will contain links instead of bbcode tags. Lowercase version.{{msg_clean}}- user/operator message without[file=616_6f13fafc726e119f5a0a3f49221b45f7]in it's body if it's the only content in message.{{msg_clean_lowercase}}- user/operator message without[file=616_6f13fafc726e119f5a0a3f49221b45f7]in it's body if it's the only content in message. Lowercase version.{{msg_html}}- msg in HTML format{{msg_html_lowercase}}- msg in HTML format lowercase{{msg_html_nobr}}- msg in HTML format without<br />tags. Presently used in telegram integration.{{msg_html_lowercase_nobr}}- msg in HTML format lowercase without<br />tags.{{custom_args_1}}- comes from trigger definitionCustom argument for the Rest API Callfield from bot trigger.
All messages at once
{{msg_all_since_transfer_content}}- Messages since chat was transferred to operator. All messages without[<date>] [<nick>]prefix within each message. System messages are not printed.{{msg_all_op_msg_content}}- All operator messages in the chat. All messages without[<date>] [<nick>]prefix within each message.{{msg_all_vis_msg_content}}- All visitor messages in the chat. All messages without[<date>] [<nick>]prefix within each message.{{msg_all_vis_since_transfer_content}}- All visitor messages in the chat since operator took over the chat. All messages without[<date>] [<nick>]prefix within each message.{{msg_all_since_transfer_content_date_nick}}- All visitor messages in the chat since operator took over the chat. All messages with[<date>] [<nick>]prefix within each message.{{msg_all}}- all chat messages. All messages with[<date>] [<nick>]and meta data including whisper messages.{{msg_all_conversation}}- all chat messages with[<date>] [<nick>]. Without system and whisper messages.{{msg_items}}- all chat messages objects encoded in JSON. Just dojson_decodeon passed variable{{msg_all_html}}- all chat messages rendered as HTML. You might need to style classes.{{msg_all_content}}- all messages without[<date>] [<nick>]prefix within each message. System messages are not printed.{skip_empty_msg}- will skip a message in{previous_visitor_messages_list_url__10__1}loop if message content is empty.{skip_media_msg}- will skip a message in{previous_visitor_messages_list_url__10__1}loop if message is considered media one. E.g it has attached file or content is file attachement.{{media_all}}- array of files attached[file...syntax.{{media_all_links}}- plain text with structure of
http://example.com/link/to/file_1.pdf [file_1.pdf]
http://example.com/link/to/file_2.pdf [file_2.pdf]
{{media_all_links_raw}}- plain text with structure of
http://example.com/link/to/file_1.pdf
http://example.com/link/to/file_2.pdf
{if_previous_visitor_messages}{"content":{{previous_visitor_messages_url__100__1}},"role":"user"},{/if_previous_visitor_messages}print last 100 messages if there is any. We print here only visitor last 100 messages. We skip very first message with1as a second argument. Offset in other words. It's an optional argument.
{previous_visitor_messages_list_url__10__1} {skip_empty_msg} {separator},{/separator} { "role": "{assistant}assistant{/assistant}{user}user{/user}", "content": {not_item_empty__args.item.msg}{{args.item.msg}}{/not_item_empty} } {end_separator},{/end_separator} {/previous_visitor_messages_list_url}- print last 10 messages and skip the most recent one. It will start rendering items after from a result set we detect a visitor message (Required by Gemini 2.5 models).
And here is an example of how this can be used with AI integration. See ChatGPT integration.
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant. You can answer questions only from https://doc.livehelperchat.com. If you don't know the answer call `knowledge_base` function"
},
{previous_visitor_messages_list_url__10__1}
{skip_empty_msg}
{separator},{/separator}
{
"role": "{assistant}assistant{/assistant}{user}user{/user}",
"content": {not_item_empty__args.item.msg}{{args.item.msg}}{/not_item_empty}
}
{end_separator},{/end_separator}
{/previous_visitor_messages_list_url}
{
"role": "user",
"content": {{msg_url}}
}
]
Reply to scenario
{reply_to},"context": { "message_id": {{iwh_msg_id}} }{/reply_to}
For this to work you have to
Enter
Messages IDin icoming webhooksMessage related attributesEnter
Reply to message IDin icoming webhooksMessage related attributesso we will know to which message visitor is replying.In
Rest API Callssection inRemote Message IDenter attribute location of send message.Reply to messages are support in official facebook whatsapp integration. So take a look there just.
Magic prefixes for replaceable variables
There are three types of magic prefixes they apply to all replaceable variables and only to body,files payload.
raw_<replaceable_variable>- will return value without wrapping quotes where content will be a valid JSON string. E.graw_{{lhc.nick}}, etc.raw_{{args.chat.id}}sensitive_<replaceable_variable>- content of variable will be processed usingMessages content protectionrules.raw_sensitive__<replaceable_variable>- content of variable will be processed usingMessages content protectionrules and wrapping quotes will be removed content will be a valid JSON string.direct_<replaceable_variable>- to content of variable will be appliedjson_decodeand if output is a string, it's content will be used. Usefull in combination with{{custom_args_1}}
Other:
{{ip}}- visitor ip. If you are running background worker this value will be localhost.{{footprint}}- last 25 viewed pages url's{{chat_id}}- chat ID{{timestamp}}- unix timestamp{{date_utc}}- date in full format in UTC timezone. E.g2024-11-20 12:27:03 UTC.{{subject_ids}}- array of subject id's assigned to chat{{subject_list}}- array of subjects objects with all attributes{{subject_list_names}}- string of subject names imploded by comma{{survey}}- filled chat surveys{{replaceable.<identifier>}}Use Replaceable variables in Rest API. E.g if your replaceable variable identifier isbrandyou can use inRest API{{replaceable.brand}}Usefull in case you want to have different system prompt or functions per department.
Do not send a request if this variable is empty
This is useful if a message from webhook does not have content, and you want to skip it. It works only for first level replaceable variables, E.g
{{msg}},{{msg_lowercase}},{{msg_url}}etc...
This happens if you use Send Typing or some other bot message which is visible in web widget but does not have any content third party integration.
Attributes usefull for sending content in Sub URL for file
{{file_body}}- base64 encoded file content'data:'.$mediaFile->type.';base64,'.base64_encode(file_get_contents($mediaFile->file_path_server));{{file_url}}- url to download file directly{{file_name}}- uploaded file name from operator
Additional attribute you can use for Sub URL for file and If you are sending file you can have a different body content
{file_api}your request body in case it's a file{/file_api}{image_api}your request body in case it's an image{/image_api}- 'image/jpeg','image/png','image/gif'{vodeo_api}your request body in case it's an image{/vodeo_api}- 'video/mp4'
You can have dynamic variable based on file extension by using {api_by_ext__<file_type>_<other_file_type>}sendVoice{/api_by_ext} E.g
{api_by_ext__ogg}sendVoice{/api_by_ext}- usesendVoicevalue if media file extension isogg{api_by_ext__mp3_m4a}sendAudio{/api_by_ext}usesendAudiovalue if media file extension ismp3orm4a
Same pattern has to be defined in Sub URL for file and If you are sending file you can have a different body content fields.
Example from telegram. Sub URL for file file url
/bot{{args.chat.incoming_chat.incoming_dynamic_array.access_token}}/{api_by_ext__ogg}sendVoice{/api_by_ext}{api_by_ext__mp3_m4a}sendAudio{/api_by_ext}{api_by_ext__mp4}sendVideo{/api_by_ext}{image_api}sendPhoto{/image_api}{file_api}sendDocument{/file_api}
Example from telegram. If you are sending file you can have a different body content file content
{
"chat_id":{{args.chat.incoming_chat.chat_external_id}},
"{api_by_ext__ogg}voice{/api_by_ext}{api_by_ext__mp3_m4a}audio{/api_by_ext}{api_by_ext__mp4}video{/api_by_ext}{file_api}document{/file_api}{image_api}photo{/image_api}":{{file_url}}
}
{not_empty__*}body if variable is not empty{/not_empty}variable{{msg_url}}has to be not empty. In this scenario we send ChatGPT additional message only if it's not empty.- As for check you can use any replaceable variables like
{{msg_url}}etc.
{
"assistant_id": "asst_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"parallel_tool_calls": false
{not_empty__msg_url},"additional_messages" : [{"role" : "user", "content" : {{msg_url}} }]{/not_empty}
}
{is_empty__*}body if variable is empty{/is_empty}variable{{msg_url}}has to be not empty. In this scenario we send ChatGPT additional message only if it's not empty.- As for check you can use any replaceable variables like
{{msg_url}}etc. In below exampel we check ifis_loggedvariable is not set. We instruct Chat GPT do not call any functions and ask user to login.
{
"assistant_id": "asst_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"parallel_tool_calls": false
{is_empty__args.chat.chat_variables_array.is_logged}
,"tools":[]
, "additional_instructions":"Visitor is not logged in and functions calls are not enable to him. You can answer questions only from documentation. Ask him to login to get personal account information. You can get personal information once visitor is logged in."
{/is_empty}
{not_empty__msg_url},"additional_messages" : [{"role" : "user", "content" : {{msg_url}} }]{/not_empty}
}
Additional attributes you can use
{interactive_api}quick reply buttons wrapper{/interactive_api}{button_template}quick reply individual button template{/button_template}{is_button}"button"{/is_button}- in case quick reply button is a button{is_url}"url"{/is_url}- in case quick reply button is an url{{rest_api_button}}- custom content from bot builderRest API button custom content.field{{button_payload}}- either lhc genrared internal payload for the trigger execution or just an URL{{button_title}}- quick reply button title
{
"receiver":{{args.chat.incoming_chat.chat_external_id}},
"min_api_version":7,
"sender":{
"name":"Live Helper Chat"
},
"type":"text",
"text":{{msg_url}}
{interactive_api}
,"keyboard": {
"Type": "keyboard",
"Buttons": [
{button_template}
{
"ActionType":{is_button}"reply"{/is_button}{is_url}"open-url"{/is_url},
"ActionBody": {{button_payload}},
"Text":{{button_title}},
"TextSize":"regular"
{{rest_api_button}}
}
{/button_template}
]
}
{/interactive_api}
}
Main chat attributes. You can access only first level attributes.
{{lhc.nick}}- visitor nick{{lhc.email}}- e-mail{{lhc.department}}- department name{{lhc.dep_id}}- department ID{{lhc.<any chat attribute>}}- all possible attributes you can find https://api.livehelperchat.com at the bottom underModels > Chatalso you can access any dynamic attribute like {{lhc.department_name}}.
To access custom passed variables or fields.
{{lhc.add.<additional variable key/identifier>}}- these values you are passing additionaly. It's eitherField identifierfromStart a chat form settings > Custom fieldsor if you are passing manually it'snameattribute. If you putField identifiervalue asgenderinStart a chat form settings > Custom fields. In Rest API Call you can access this field like{{lhc.add.gender}}{{lhc.var.<chat variable key>}}- these values can be set using extensions etc. It's data is taken byjson_decodefunction fromchat_variablescolumn value. This column stores JSON as{<key> : <value>,..}. Usually in this column extensions stores their own data.{{media}}- Will hold JSON encoded related files to send message.
[
{
"id": 636,
"size": 10007,
"upload_name": "image.png",
"type": "image/png",
"extension": "png",
"hash": "4bcda854ef4f27e8b4003b42c84f1cb6",
"url": "https://devmysql.livehelperchat.com/file/downloadfile/636/4bcda854ef4f27e8b4003b42c84f1cb6"
}
]
Dynamic attributes extraction. You can go as deep as you want.
{{args.<any argument attribute>.<any subargument attribute>}}- if you are implementing webhooks most likely you will be using this as placeholder.{{args.chat.department.identifier}}- This way you can access any chat and child object attributes. In this example department identifier.{{args.chat.department}}- you can pass even all department object.{{args.chat.chat_variables_array.order_id}}- accessorder_idif field is defined asThis variable is invisible for operator and will be stored in chat_variables attribute{{args.chat.id}}Chat object also see__getmethod for magic attributes likedepartmentoruser{{args.chat.user.name_support}}name visible in the widget or{{args.chat.user.name_official}}name visible in the back office
{{args.arg_1}}- commands arguments{{args.replace_array.arg_1}}- replaceable variables. E.g if you define custom chat variables you can use them in Rest API calls.
Incoming chat attributes. This is usefull if you want to access to payload attribute of Incoming webhook created chat.
{{args.chat.incoming_chat.chat_external_id}}- external chat id{{args.chat.incoming_chat.chat_external_first}}- first part of chat external if two fields are used{{args.chat.incoming_chat.chat_external_last}}- last part of chat external if two fields are used{{args.chat.incoming_chat.payload_array.*}}- you can access any first payload attribute. E.g session Id{{args.chat.incoming_chat.incoming.attributes.<you defined key in attribtues of incoming webhook>}}- you can use this as placeholder forSub URLorSub URL for file. Just leave empty host attribute.{{args.chat.incoming_chat.incoming.scope}}- you can access any attribute of incoming webhook definition{{args.msg_text}}- unknown button click payload value
All possible models attributes you can find https://api.livehelperchat.com at the bottom under Models > Chat
These are the main classes
args.chat.<attr>args.chat.user.<attr>args.chat.department.<attr>args.chat.incoming_chat.<attr>args.chat.incoming_chat.incoming.<attr>
All classes can be found here
Example
So your JSON body in rest API can look like
{
"msg":{{msg}}, // OR {{msg_clean}}
"query":{{query}},
"media":{{media}},
"subject_ids": {{subject_ids}}
}
Replaceable variables works only in
- Params
- Body
- Headers
Trigger workflow
In trigger once everything is setup it will look like this.
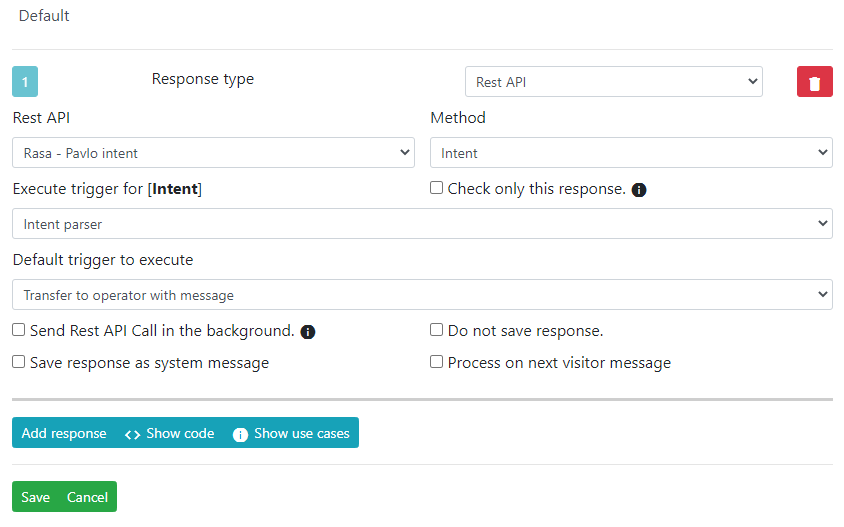
Fields description
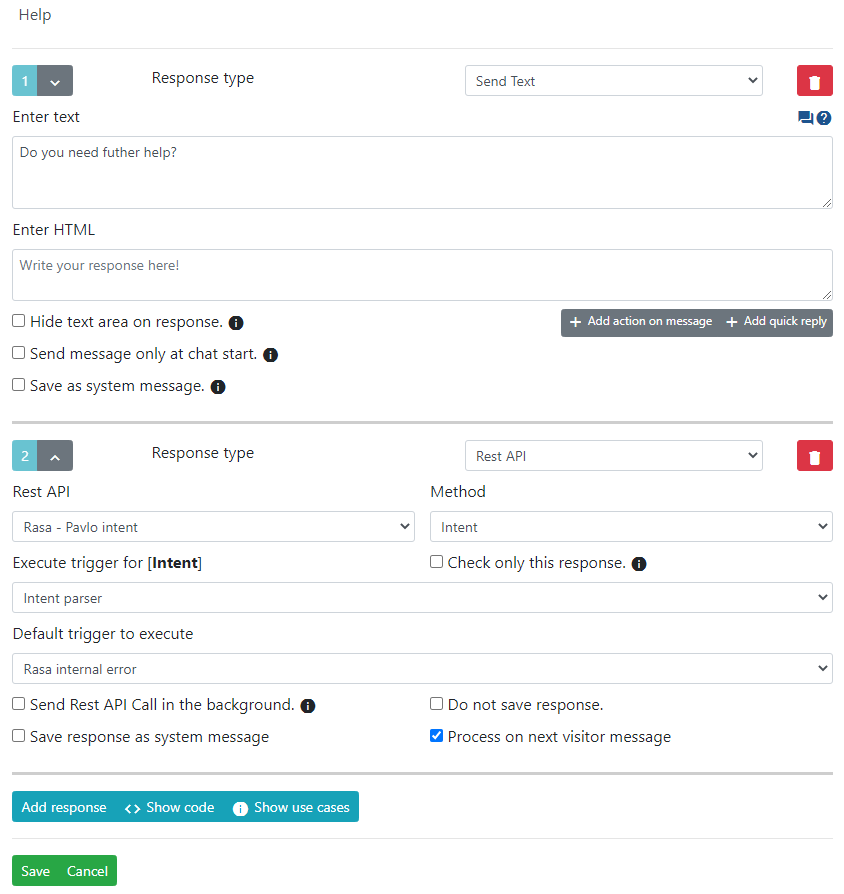
Rest API- it's our main Rest APINamewe are working withMethod- it's ourName of the requestfrom Rest API building window.User entered parameter- it's just defined parameter which is coming from Rest API builder windowUser parameterstab.Execute trigger for [UUID Set]- It's defined output parsing option which we defined in Rest APIOutput parsingtab.Default trigger to execute- if we did not found any matching output combination this trigger will be executed.Send Rest API Call in the background.- by defaultRest APIcalls are send as soon visitor sends a message, they are happening on same request. This can lead to a problems if Rest API is slow. We can send Rest API calls in the background, but for that you have to be running lhc-php-resque extension. You won't need to code anything just setup extension itself.Process on next visitor message- this call will be executed only on next visitor message. Usefull in case you want to check only for specific actions.Save response as system message- will save a message as system message. It will be invisible for the visitor.Do not save response.- usefull in case you want to execute a call, but do not save any related information.Custom argument for the Rest API Call- this content can be reached via Rest API call directly through{{custom_args_1}}var. It's usefull in ChatGPT integration- If your Rest API fails you can just have something like this
{"success":false,"reason":"service is temporrary offline, try after 5 minutes"} - Or you can forward direct response from Your Rest API
{"success":true,"list":{content_1}}Take a look https://github.com/LiveHelperChat/chatGPT
- If your Rest API fails you can just have something like this
Example of Process on next visitor message
Output variables in triggers
Use can use these variables in your text triggers response text.
{content_1}{content_2}{content_3}{content_4}{content_5}{content_6}{http_code}- https status code returned from request{http_error}- additional error explanation fromcurl_error($ch);{content_raw}- raw response returned from Rest API call without any parsing{http_data}- Request parameters used for rest api call.
How to iterate through response if content_[n] holds an array?
Text message content can look like this. Your iterable object will be available under {args.item.<internal property of you object> attribute.
{foreach=content_1}
- {args.item.mail_asesor}
{/foreach}
There variables can be used in most of the response types including
- Set main chat attribute for setting
email,nick,phoneetc. - Set additional chat attribute for custom chat attributes
- Text responses for showing visitor information for the user itself. E.g package location
How to pass in what language chat is going?
Best way is just to pass {{args.chat.chat_locale}} if customer is chatting in any other language than english, and you pass lang argument it's value will be always content_language attribute from siteaccess settings.
- https://github.com/LiveHelperChat/livehelperchat/blob/master/lhc_web/settings/settings.ini.default.php#L154
- If you wish to pass strictly
enon english language you can just define anothersiteacessfor english language and make it default. Then in embed code passeng/as language. Live Helper Chat will see it's not the defaultsiteacessand will set chat locale to siteacesscontent_langaugevalue.
How to find out problems with Rest API
Audit log
- Newer version has option in Rest API configuration check
Log all request and their responses in audit log. - After that you will see all request made by your chosen Rest API in Audit log
Triggers
- Setup output combination for success call.
- In default response have two text messages as response
In rest api define trigger for Unknown unmatched output combination
In response have something like this. Pay attention second text message is send as system message.
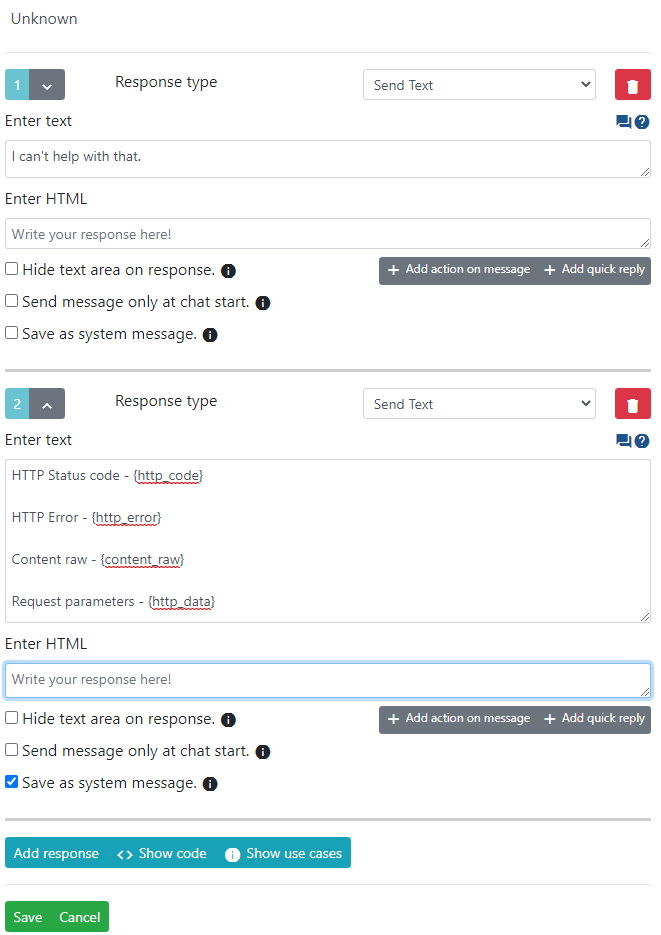
How to handle API Errors?
There is two ways to handle API errors.
- Set fallback trigger on
Default trigger to execute. If API works correctly your defined output combination will be executed. - You can just in your
Rest-APIconfiguration checkLog all request and their responses in audit log.orLog all request and their responses as system messages.. This way you will see all requests made by your Rest API in Audit log.
Events you can listen
See this extension sample https://github.com/LiveHelperChat/lhcrestapi
You can also see directly in the code for the events it dispatches https://github.com/LiveHelperChat/livehelperchat/blob/master/lhc_web/lib/core/lhgenericbot/actionTypes/lhgenericbotactionrestapi.php