Conditions
Introduction
Conditions allow you to define predefined criteria that can be used in multiple places, such as:
- The
Check for conditions to proceedbot response type. - Chat priority settings.
Conditions are checked using a specific syntax:
{condition.<condition_identifier>} (e.g., {condition.is_vip}).
The result of a condition check will be either valid or not_valid.
Conditions can also check other conditions during their evaluation. For example:
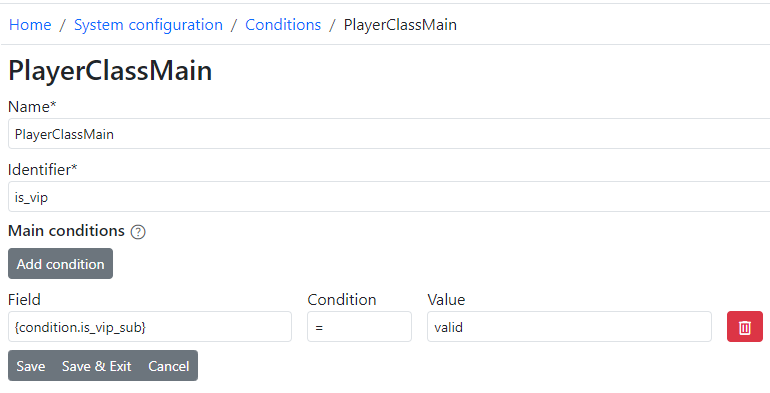
Chat Attribute Extraction
You can extract any chat attribute using this modal window:
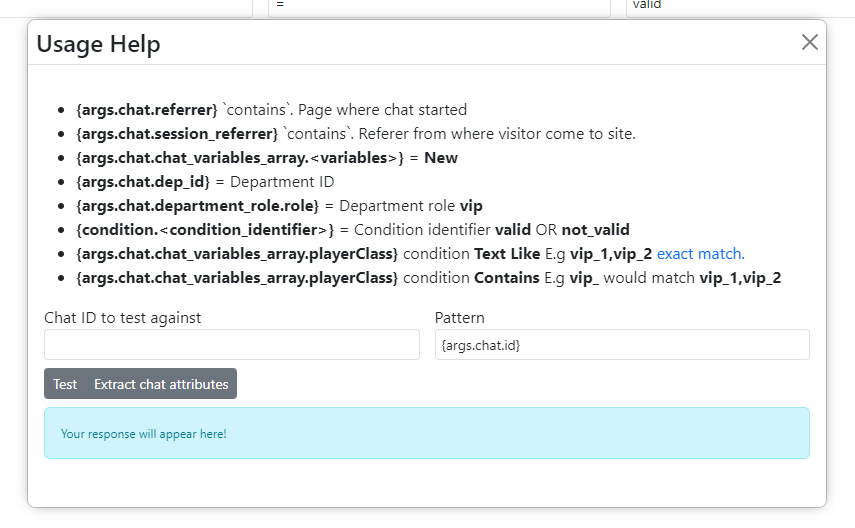
Condition Explanations
The following explanations apply to all condition checks.
= or != for Number and String Comparison
These operators perform equality checks. They require an exact match and can be used to compare numbers or strings.
For example, to check if a chat department's identifier is equal to my_storage:
{args.chat.department.identifier} = 'my_storage'
To check if a chat variable pid is equal to my_pid:
{args.chat.chat_variables_array.pid} = 'my_pid'
To check the response of a REST API call:
{content_1} != 1
>, >=, <, <= for Number Comparison
These operators perform numerical comparisons.
For example, to check if a chat's duration is more than 5 seconds:
{args.chat.chat_duration} > 5
Text like and Text not like
These operators, internally referred to as like and notlike, perform pattern matching on text.
The rules for these operators are defined here.
For example:
{args.chat.department.name} Text like edas && em [params max_words=2]
This condition checks if the department name contains exactly two words, edas and em.
To match any value from a list of values, use:
{args.chat.nick}Text likeremdex,vip_player(checks if the chat nick is eitherremdexorvip_player).
{args.chat.dep_id}Text like5,8(matches if the department ID is 5 or 8).
You can use any variable from Check for conditions to proceed
Contains
This operator checks if a string contains another string as a substring.
Live bot migration using actions conditions
This is extremely useful in case you have a bot and to migrate some of its flows without creating a new bot.
- You can use E.g
is_lt_userto expecting condition to be valid - You can use E.g
-is_lt_user(-) prefix for expecting condition to be invalid
Date range use case
You can have conditions which work based on date
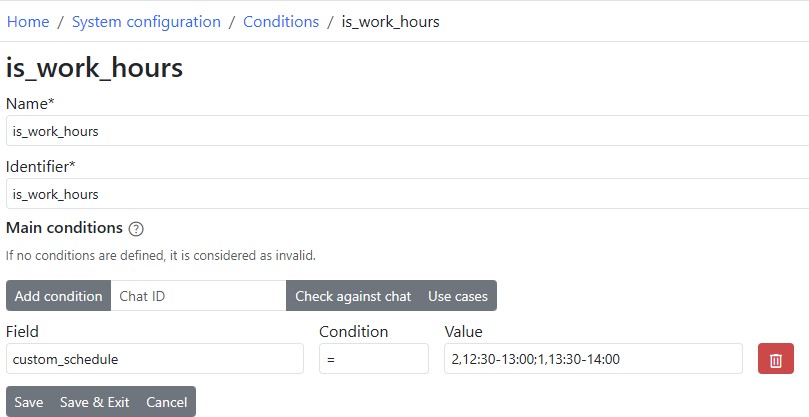
After you have a defined condition, you can use it in trigger
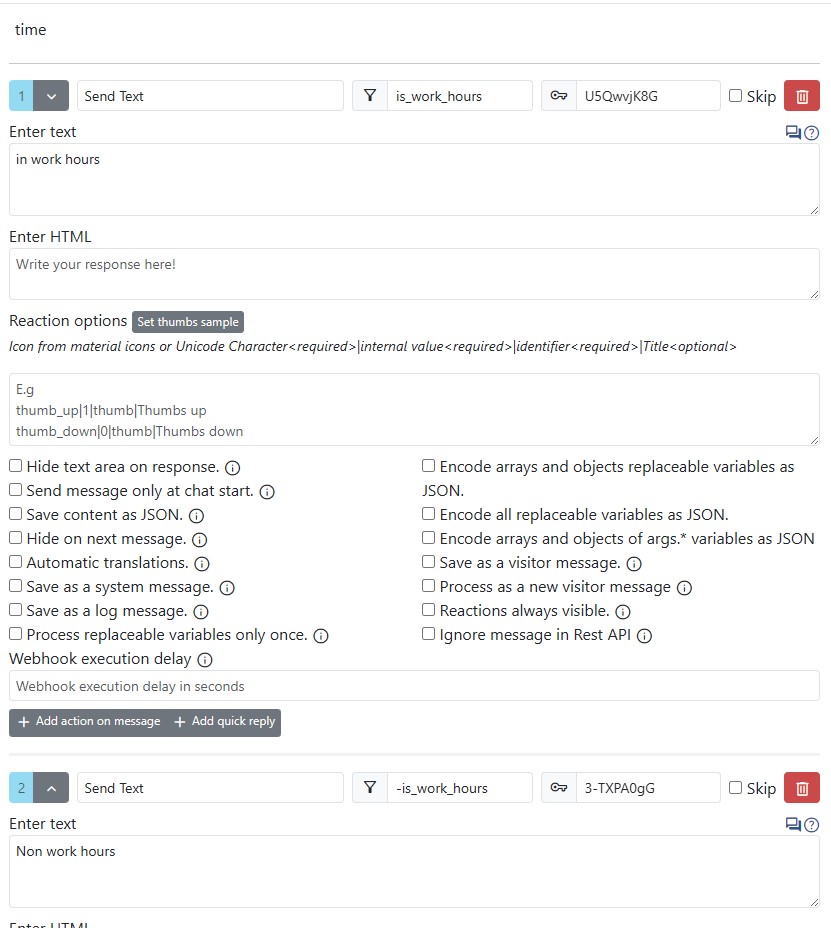
Bot Example
Example usage in a bot:
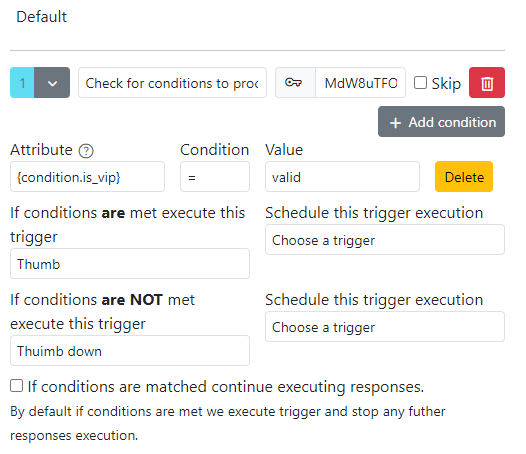
Bot Example with Buttons Using Conditions
This example demonstrates a quick reply button with a condition. The button is displayed only if the bot_not_answered condition is met.
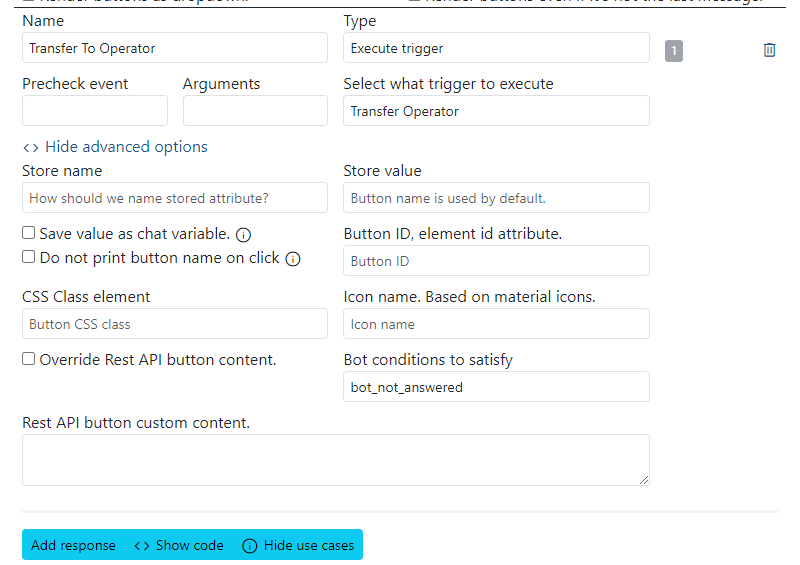
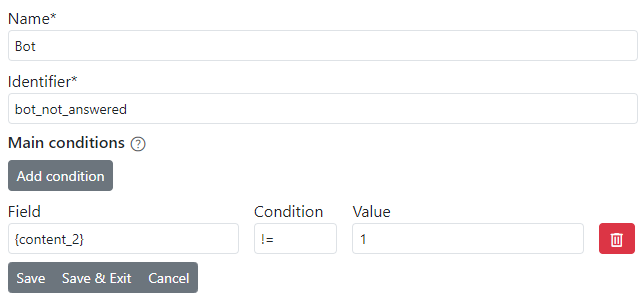
The condition is defined as follows:
Permissions
The following permissions are required:
lhgenericbot,manage_conditions